Anti-inflammatory drugs are the drugs used to reduce inflammation and pain for the management of edema and tissue-damaging. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) and non-narcotic analgesics are other names for them.

Chemically, it is sodium [0-(2,6 –dichloroanilino) phenyl] acetate. It inhibits COX-2 with more efficacy than COX-1 inhibitors and has fewer GI side effects than aspirin.
Uses
As an anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic agent.
Side effects
Nausea, vomiting, ulceration, headache.

Because it lacks the benzylic methyl group, it has a half-life of 4 to 6 hours and is not vulnerable to oxidation.
Uses – in the management of post-operative pain.
Side effects – stomach pain, GI irritations, ulcers.

Pain, fever, and inflammation are treated with this non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Mechanism of action –
PTGS1 and PTGS2 encode the cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 that ibuprofen inhibits in a non-selective and reversible manner.
Uses –
In the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, analgesic, and antipyretic. It should not be taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding since it can enter the foetal circulation and breast milk. It is less prone to cause GI ulcers than salicylates.

Chemically, Naproxen is naphthyl 6-methoxyisopropionic acid. It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, anti-rheumatic, analgesic, anti-dysmenorrhoeal, and vascular headache suppressant.
Naproxen is having (partly) an ability to inhibit COX-1 and COX-2. In addition to blocking the cyclooxygenase (Prostaglandin synthase) enzyme, it also lowers the formation of prostaglandins by catalyzing the conversion of arachidonic acid to endoperoxides.
SAR
COOH group is essential for the activity. Replacement of this group diminishes or abolishes the activity.
The anti-inflammatory activity of COOH compounds will increase if the acidity of the group increases. Decreases in acidity will decrease anti-inflammatory activity.
The Presence of an indole ring is necessary for the activity. Substitution at the C5 position (R2) by fluro, methyl, dimethylamino0, alkoxy, or acetyl group increases the activity. Alkyl group at C2 position increases activity as compared to aryl groups. Substitution at the acetic acid chain gives compounds of greater activity. E.g. Indomethacin, sulindac, ketorolac, etc.
Presence of methoxy at –C5 position group on the ring, methyl at C2 position, dimethyl amino group at C5- position in indole moiety of indomethacoin exhibit activity.
A phenyl group with a chlorinated or fluorinated group at the para position also has anti-inflammatory properties.

It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine (NSAID) used to treat the pain and inflammation of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
WARNING
Piroxicam should not be used just before or after bypass heart surgery. It may be fatal. Also, the wrong use of this drug can cause intestinal bleeding that can cause the death of the person.
USES
Osteoarthritis (arthritis caused by a breakdown of the cartilage lining the joints) and rheumatoid arthritis are two illnesses for which this drug is prescribed (arthritis caused by swelling of the cartilage lining the joints). Piroxicam belongs to the class of drugs known as NSAIDs.

Chemically, it is p-ethoxyacetamilide. It was introduced in 1885 to medicine. It causes hemolytic anemia and meth-haemoglobinanemia. Due to its side effects, which include an increased risk of some malignancies and renal impairment, its usage has decreased. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is the product of its metabolism.
Uses
Analgesic, and anti-pyretic activity
Side effects – include GI irritation.

It is also called paracetamol. N-acetyl-p-aminophen is its chemical name. Phenacetin is its substrate. It inhibits the cyclooxygenase enzyme centrally but has a less effect peripherally.
Mechanism of action of paracetamol
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
Penetrates the blood-brain barrier
Blocks cyclooxygenase (COX3) in the brain
Prostaglandins (PGE) synthesis and release in the central nervous system are inhibited.
Inhibits the action of endogenous pyrogens on the heat-regulating centers in the brain.
Antipyretic effect
Uses
Analgesic and anti-pyretic activity
Side effects
Liver toxicity in chronic alcoholics.

Chemically, it is 2,3-dimethyl – 1-phenyl-3-pyrazoline-5-one. A synthetic compound that was used in medicine for the first time. Powdery white, colorless powder with a slight bitter taste. It has no odor or color. Hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, and chloroform are all freely soluble in it.
Uses
Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic activities.
Side effects
Include GI irritation, swelling, and vomiting.
They are anti-inflammatory drugs, also possess some analgesic and anti-pyretic activities. They also have a little uricosuric effect.
Uses
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are treated with phenylbutazone.
Side effects
Due to bone marrow depression, the duration of treatment should be limited to seven to ten days.
Diclofenac
STRUCTUREChemically, it is sodium [0-(2,6 –dichloroanilino) phenyl] acetate. It inhibits COX-2 with more efficacy than COX-1 inhibitors and has fewer GI side effects than aspirin.
Uses
As an anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic agent.
Side effects
Nausea, vomiting, ulceration, headache.
Ketorolac
STRUCTUREBecause it lacks the benzylic methyl group, it has a half-life of 4 to 6 hours and is not vulnerable to oxidation.
Uses – in the management of post-operative pain.
Side effects – stomach pain, GI irritations, ulcers.
Ibuprofen
STRUCTUREPain, fever, and inflammation are treated with this non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Mechanism of action –
PTGS1 and PTGS2 encode the cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 that ibuprofen inhibits in a non-selective and reversible manner.
Uses –
In the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, analgesic, and antipyretic. It should not be taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding since it can enter the foetal circulation and breast milk. It is less prone to cause GI ulcers than salicylates.
Naproxen
STRUCTUREChemically, Naproxen is naphthyl 6-methoxyisopropionic acid. It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, anti-rheumatic, analgesic, anti-dysmenorrhoeal, and vascular headache suppressant.
Naproxen is having (partly) an ability to inhibit COX-1 and COX-2. In addition to blocking the cyclooxygenase (Prostaglandin synthase) enzyme, it also lowers the formation of prostaglandins by catalyzing the conversion of arachidonic acid to endoperoxides.
SAR
COOH group is essential for the activity. Replacement of this group diminishes or abolishes the activity.
The anti-inflammatory activity of COOH compounds will increase if the acidity of the group increases. Decreases in acidity will decrease anti-inflammatory activity.
The Presence of an indole ring is necessary for the activity. Substitution at the C5 position (R2) by fluro, methyl, dimethylamino0, alkoxy, or acetyl group increases the activity. Alkyl group at C2 position increases activity as compared to aryl groups. Substitution at the acetic acid chain gives compounds of greater activity. E.g. Indomethacin, sulindac, ketorolac, etc.
Presence of methoxy at –C5 position group on the ring, methyl at C2 position, dimethyl amino group at C5- position in indole moiety of indomethacoin exhibit activity.
A phenyl group with a chlorinated or fluorinated group at the para position also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Piroxicam
STRUCTUREIt is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine (NSAID) used to treat the pain and inflammation of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
WARNING
Piroxicam should not be used just before or after bypass heart surgery. It may be fatal. Also, the wrong use of this drug can cause intestinal bleeding that can cause the death of the person.
USES
Osteoarthritis (arthritis caused by a breakdown of the cartilage lining the joints) and rheumatoid arthritis are two illnesses for which this drug is prescribed (arthritis caused by swelling of the cartilage lining the joints). Piroxicam belongs to the class of drugs known as NSAIDs.
Phenacetin
STRUCTUREChemically, it is p-ethoxyacetamilide. It was introduced in 1885 to medicine. It causes hemolytic anemia and meth-haemoglobinanemia. Due to its side effects, which include an increased risk of some malignancies and renal impairment, its usage has decreased. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is the product of its metabolism.
Uses
Analgesic, and anti-pyretic activity
Side effects – include GI irritation.
Acetaminophen
STRUCTUREIt is also called paracetamol. N-acetyl-p-aminophen is its chemical name. Phenacetin is its substrate. It inhibits the cyclooxygenase enzyme centrally but has a less effect peripherally.
Mechanism of action of paracetamol
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
Penetrates the blood-brain barrier
Blocks cyclooxygenase (COX3) in the brain
Prostaglandins (PGE) synthesis and release in the central nervous system are inhibited.
Inhibits the action of endogenous pyrogens on the heat-regulating centers in the brain.
Antipyretic effect
Uses
Analgesic and anti-pyretic activity
Side effects
Liver toxicity in chronic alcoholics.
Antipyrine
STRUCTUREChemically, it is 2,3-dimethyl – 1-phenyl-3-pyrazoline-5-one. A synthetic compound that was used in medicine for the first time. Powdery white, colorless powder with a slight bitter taste. It has no odor or color. Hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, and chloroform are all freely soluble in it.
Uses
Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic activities.
Side effects
Include GI irritation, swelling, and vomiting.
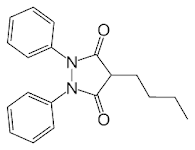
Phenylbutazone
STRUCTUREThey are anti-inflammatory drugs, also possess some analgesic and anti-pyretic activities. They also have a little uricosuric effect.
Uses
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are treated with phenylbutazone.
Side effects
Due to bone marrow depression, the duration of treatment should be limited to seven to ten days.
Get subject wise printable pdf notesView Here



No comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't spam. Comments having links would not be published.