By eliminating compounds with double or triple bonds between carbon atoms, saturated compounds transform into unsaturated compounds. Sulphur compounds can also be made via the elimination reaction. Alkenes can also be synthesized using this method.
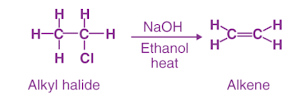
Elimination reactions involve removing several atoms from a molecule, either as a pair or as a group. The oxidation of metals is typically accomplished by using acids and bases, or the oxidation of metals is accomplished by using acids and bases. High temperatures can also be used to remove acids and bases.

E-1 mechanism shares features with SN1 reaction. Firstly, leaving groups are removed to form carbocation intermediates. Having the slowest step in the reaction, it determines the entire reaction rate.
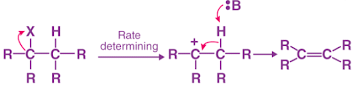
The E2reaction rate is determined as,
Rate = k[Rx][Base]
Therefore, both the substrate (RX) and the base affect the rate of the reaction. The most stable alkene is produced after removing the most unstable alkene.
Elimination reactions involve removing several atoms from a molecule, either as a pair or as a group. The oxidation of metals is typically accomplished by using acids and bases, or the oxidation of metals is accomplished by using acids and bases. High temperatures can also be used to remove acids and bases.
Important methods in elimination reaction
Elimination reactions usually differ from one another based on the type of atoms or groups of atoms that leave a molecule. Due to this, this type of reaction involves two basic methods;- Dehydrohalogenation
- Dehydration
E1 reaction
- Two main steps are usually involved in a monomolecular elimination reaction like the E1: ionization and deprotonation.
- Carbocation intermediates are formed during ionization. Carbocations involve the loss of protons due to deprotonation.
- Molecular pi-bonds are formed when this happens in the presence of a base.
- E1 also mentions that the concentration of the substance being transformed affects the rate of conversion.
E-1 mechanism shares features with SN1 reaction. Firstly, leaving groups are removed to form carbocation intermediates. Having the slowest step in the reaction, it determines the entire reaction rate.
E2 reaction
- It is essentially a one-step process in a bimolecular elimination mechanism (E2).
- In this case, a new double bond forms when the hydrogen-carbon and carbon-halogen bonds break apart.
- As part of the rate-determining step of the E2 mechanism, a base has a great deal of influence.
- A large part of the reaction rate depends on both the elimination agent concentration and the substrate concentration.
- It possesses second-order kinetics.
The E2reaction rate is determined as,
Rate = k[Rx][Base]
Therefore, both the substrate (RX) and the base affect the rate of the reaction. The most stable alkene is produced after removing the most unstable alkene.
Alkyl halides in order of reactivity
RI > RBr > RCl are the most reactive alkyl halides.- Carbon atoms are attached to halogen atoms in alkyl halides.
- Their formula is generally R-X
- In this case, R stands for alkyl group, and X stands for Cl, Br, I or F.
- Halogen atoms are attached to carbon in alkyl halides to form the functional group.
- A primary alkyl halide has 1 carbon atom attached to one of the carbon atoms of the carbon chain, a secondary alkyl halide has 2 carbon atoms attached to the carbon chain, and a tertiary alkyl halide has 3 carbon atoms attached to the carbon chain.
- The reactivity of alcohols with halogen acids is ranked according to their length: tertiary alcohols exhibit higher reactivity than secondary alcohols, while primary alcohols exhibit lower reactivity.
Get subject wise printable pdf notesView Here


No comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't spam. Comments having links would not be published.