Basicity
Nitrogen in amines is electron-dense because of the lone pair electrons, as shown by the red color in the electrostatic potential map to the left. Acids are electron-poor and react easily with basic amino acids.The following equation shows that when a proton is transferred to an amine, ammonia and water will react, yielding an ammonium salt and a hydroxide ion:
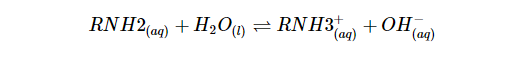
Known also as the base dissociation constant (Kb), the equilibrium constant for this reaction is:

Using the same method as described in Section 2-8 to calculate a carboxylic acid's acid strength, we can determine an amine's base strength by defining analogous basicity constant. If Kb is larger and pKb is smaller, then proton-transfer equilibrium is more favorable and the base is stronger.

Known also as the base dissociation constant (Kb), the equilibrium constant for this reaction is:
Using the same method as described in Section 2-8 to calculate a carboxylic acid's acid strength, we can determine an amine's base strength by defining analogous basicity constant. If Kb is larger and pKb is smaller, then proton-transfer equilibrium is more favorable and the base is stronger.
Effect of substituent on basicity
- An amine is basic because each atom possesses two electrons that can be shared with another atom. The nitrogen atom is surrounded by an electron density created by these unshared electrons.
- An electron-rich molecule is more basic than one with few.
- Using a positive inductive effect, electron-donating or supplying groups like alkyl groups (-H3, etc.) will result in increased basicity, while electron removing groups like -NO2, etc. will decrease the basicity of the molecule.
- Due to the electron density created around the nitrogen atom of the amine, its electron-releasing capabilities increase due to the electron-donating properties possessed by the attached alkyl group.
- Alkylamines, because they release electrons more easily and more readily, are therefore more basic than ammonia.
- Basicity – order: NH3<1<2<3
Steric hindrance
- The number of alkyl groups in an alkyl group is greater than the number of hydrogen atoms.
- Alkyl groups prevent hydrogen atoms from attacking them, thus decreasing the molecule's basicity.
- Alkyl groups are a measure of basicity, and the more there are, the slower it will be.
- As a result, amines are ordered ascendingly: tertiary amine < secondary amine < primary amine.
Salvation effect
- It is a relatively strong base, and its aqueous solutions are fairly straightforward.
- Aqueous and gaseous solutions have different basicity orders due to hydrogen bonding (solvation effects).
- Hydroxide and ammonium ions can be produced by absorption of a proton by amines.
Get subject wise printable pdf notesView Here

Ankur Choudhary is India's first professional pharmaceutical blogger, author and founder of pharmaguideline.com, a widely-read pharmaceutical blog since 2008. Sign-up for the free email updates for your daily dose of pharmaceutical tips.
.moc.enilediugamrahp@ofni :liamENeed Help: Ask Question

No comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't spam. Comments having links would not be published.