A pH meter is used to determine the acidity or alkalinity of the solution. pH is the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. A solution containing more H+ ions remains acidic while the solution containing more OH- ions remains alkaline. pH value of solutions ranges from 1 to 14.
pH meter is used to determine the pH of different solutions in pharmaceuticals. It is more accurate method than the pH strip. A pH meter contains a pH probe that passes the electrical signals to the pH meter and pH meter displays the pH value of the solution.
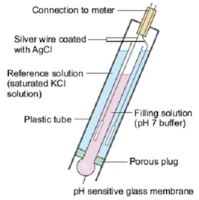
The glass pH probe contains two electrodes, a sensor electrode and a reference electrode. These electrodes are in the form of glass tubes one contains pH 7 buffer and other contains saturated potassium chloride solution. The sensor electrode bulb is made up of porous glass or permeable glass membrane coated with silica and metal salts.
A silver wire coated with silver chloride is immersed in pH 7 buffer in the bulb. Another silver wire coated with silver chloride is immersed in the saturated potassium chloride solution in reference electrode as shown in the figure.
When the probe is placed in a solution to measure the pH, hydrogen ions accumulate around the bulb and replace the metal ions from the bulb. This exchange of ions generates some electric flow that is captured by the silver wire.
The voltage of this electric flow is measured by the pH meter by converting it into pH value by comparing the generated voltage with the reference electrode.
Increase in acidity of the solution has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions that increases the voltage. This increased voltage decreases the pH reading in pH meter.
In the same manner, an increase in alkalinity decreases the hydrogen ions or increase in hydroxyl ions concentration also decreases the voltage and increases the pH value in pH meter.
The overall working principle of pH sensor and pH meter depends upon the exchange of ions from sample solution to the inner solution (pH 7 buffer) of glass electrode through the glass membrane. The porosity of the glass membrane decreases with the continuous use that decreases the performance of the probe.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't spam. Comments having links would not be published.