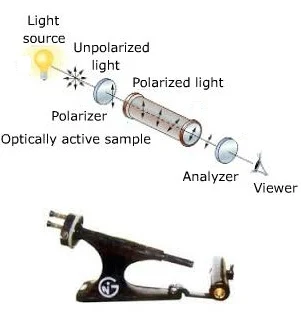
Chiral molecules are able to rotate the plane polarized light and this quality of these molecules is known as optical activity. Optical activity is measured by polarimeter. Polarimeter has a light source, polarizing filter, sampling tube and analyzing lens. Molecules having optical activity are known as optically active molecules.
Molecules those rotate the plane polarized light to the clockwise are called dextrorotary (d) or (+) but when the molecules rotate the plane polarized light to anticlockwise are called levorotary (l) or (-).
 When both dextrorotary and levorotary isomers are found in the same amount in the mixture, it is called racemic mixture. Racemic mixtures are optically inactive.
When both dextrorotary and levorotary isomers are found in the same amount in the mixture, it is called racemic mixture. Racemic mixtures are optically inactive.
The angle of rotation of plane-polarized light from its plane is known as the angle of rotation. All optically active molecules have unique ability to rotate the plane polarized light. Therefore they have an identical angle of rotation.
This feature of the molecule is used to identify the substances in pharmaceuticals. Sometimes substances are analyzed for assay using the optical rotation. Optical rotation depends upon the concentration of sample solution and path length through which light passes.
Related: Calibration of Polarimeter
The polarimeter is used to determine the optical rotation. Polarimeter has a sodium light source with the wavelength of 589.3 nm and a sample tube of 1 decimeter (1d=10cm). There are many raw materials those are identified using polarimeter. The angle of rotation is recorded at 25°C and specific optical rotation of sample is calculated using following formula.
100 x α x 100
[α]25°D = -----------------------------
LC x (100 - LOD)
Where,
α = Corrected observed rotation
D = D-line of sodium light
L = Length of Polarimeter tube in dm
C = Concentration of the substance (in %)
Correction of rotation = Av. Observed reading - Av. Blank reading


No comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't spam. Comments having links would not be published.